Robot Teleop using PS4 controller
(work in progress)

Pre-setup
Connect device to bluetooth
From GUI
Connect the controller to the robot via Bluetooth. For the first time, this can be done using Ubuntu Bluetooth GUI tool with the help of a screen (connected to the Nano via HDMI port) or via VNC. After that, the next time the controller is turned on, it will connect automatically to the robot.
The jstest-gtk is a handy GUI tool to verify if the controller is recognized by the system, install it using the following command:
sudo apt-get install jstest-gtk
If everything is OK, you can visualize which buttons and axis are pressed with the tool as shown in the following figure:
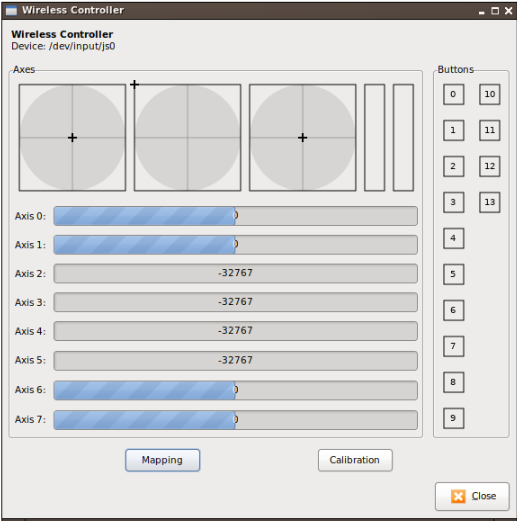
Normally, the DS4 controller is registered in the system as /dev/input/js0.
From command line
First identify the bluetooth device:
hcitool dev
# Devices:
# hci0 BC:A8:A6:D1:28:4B
Normally, on the Jetson Nano, there will be one hci0 bluetooth device.
Put the PS4 controller to paring mode (Option + Share), from the Nano scan the device using:
hcitool -i hci0 scan
The Wireless Controller device should be shown
Scanning ...
00:1F:E2:E6:24:D5 Wireless Controller
Pair the device use
bluetoothctl
[bluetooth]# pair 00:1F:E2:E6:24:D5
Now we need to trust the device
[bluetooth]# trust 00:1F:E2:E6:24:D5
[CHG] Device 00:1F:E2:E6:24:D5 Trusted: yes
Now connect to the device if it is not connected
[bluetooth]# connect 00:1F:E2:E6:24:D5
Attempting to connect to 00:1F:E2:E6:24:D5
Connection successful
Install joys ROS packages
Now we have the controller connected, to use it in ROS, we need to install two packages:
ros-foxy-joy-linux: this package allows to interface a generic Linux joystick to ROS2. Thejoy_linux_nodenode of the package will publish Joy messages on a topic called/joy. These messages contain the current state of each one of the joystick's buttons and axes..ros-foxy-teleop-twist-joy: this package is to provide a generic facility for tele-operating Twist-based ROS2 robots with a standard joystick. It converts joy messages - from the joy node - to velocity commands.
sudo apt-get ros-foxy-joy-linux ros-foxy-teleop-twist-joy
After installing the packages, the jarvis user should be added to the group input to allow default read/write permission on the joystick:
sudo usermod -aG input jarvis
# reboot for the change to take effect
sudo reboot
To test if the joy node is able to pull data from the joy stick, run:
ros2 run joy_linux joy_linux_node
on another terminal run:
ros2 topic echo /joy
Press a button or axis on the controller, the command should output the Joy message as follow:
header:
stamp:
sec: 1610838039
nanosec: 498450083
frame_id: joy
axes:
- -0.0
- -0.0
- -0.35972166061401367
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 1.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
buttons:
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 1
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
---
To test the teleop_node of the ros-foxy-teleop-twist-joy, keep the joy node running, on another terminal execute:
ros2 run teleop_twist_joy teleop_node

This node will subscribe to the /joy topic and convert joy stick commands to Twist messages published on the /cmd_vel topic.
These message can be displayed via the command:
ros2 topic echo /cmd_vel
Example output:
linear:
x: -0.011655661277472973
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: -0.0
---
linear:
x: -0.017084743827581406
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: -0.0
Note that, by default the
teleop_nodeuses the PS3 configuration profile, to issue a command with the controller, hold the R1 button (button 5 on jstest-gtk), and press the right Axis.
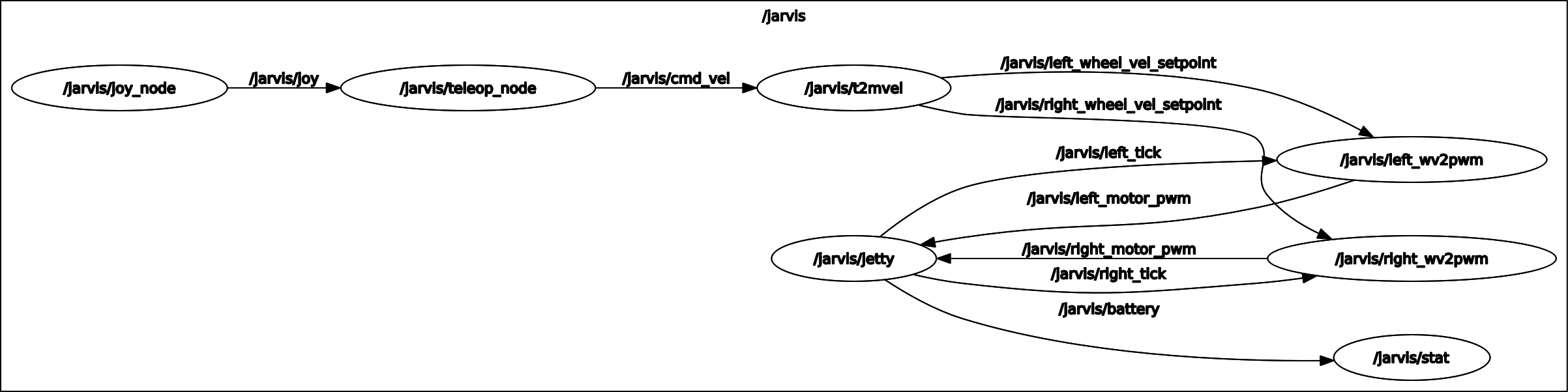
Teleop Jarvis with the controller
Except the two dependent packages installed above, all other necessary RO2 2 nodes are implemented in the jarvis_core package. The teleop stack can be launched via:
cd ~/workspace/ros2
. install/setup.sh
ros2 launch jarvis_core core.py
The robot is now fully controlled via the PS4 controller.
The following sub-sections will present insight detail of the teleop stack implementation.
Comments
The comment editor supports Markdown syntax. Your email is necessary to notify you of further updates on the discussion. It will be hidden from the public.